JSTOR Tutorial
JSTOR is an easy-to-use database that provides access to multidisciplinary scholarly articles, books, reviews, and primary sources. There is a waiting period, called the "moving wall," between when articles are published and when they are available through JSTOR, which typically ranges from 3 to 5 years. JSTOR does not search newspaper or popular magazine articles.
- Basic Search
-
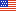
To conduct a basic search within JSTOR, start by entering keywords in the search bar. JSTOR automatically searches full text and puts the word "and" between terms. To search for a phrase or exact wording, put quotes around the terms.
- Advanced Search
-
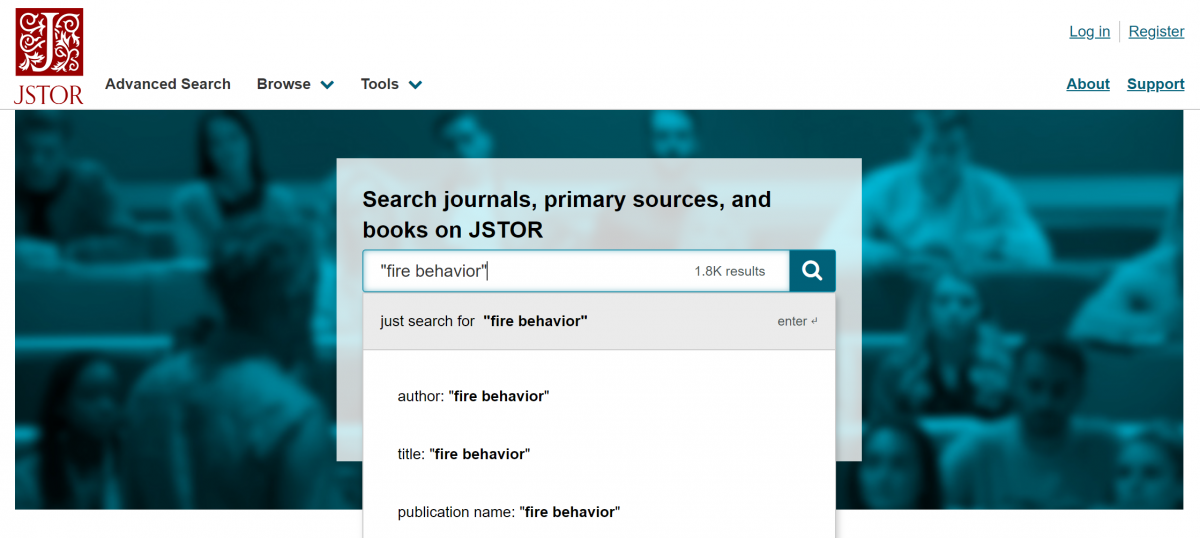
To conduct an advanced search, click on Search at the top of the page or select Advanced Search from the Search dropdown menu. Search for terms found in the body of the article (in the "full-text" field) or for author, title, abstract, or image caption. Searching for a term in the abstract or caption fields will limit results only to items that have an abstract or image caption. For broadest searching, search for terms in the "full-text" field.
- Broaden a search
-
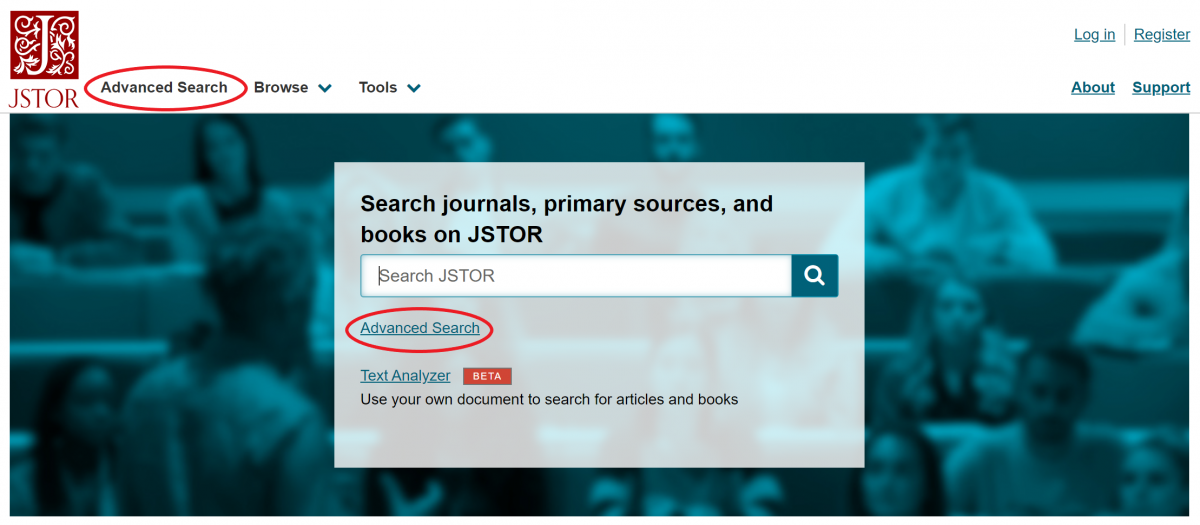
Narrow or broaden a search by using Boolean operators AND, OR, and/or NOT; learn more about these terms on the BLM Library's Search Tips page. Add up to five additional search fields by using the Add Field + button. JSTOR's Advanced Search also enables users to search for terms that are within 5, 10, or 25 words of each other by using the NEAR 5, NEAR 10, or NEAR 25 operators. For example, the query below will return results with the term "drought" appearing within 5 words of the term "Colorado" in the body of the article ("full-text"). Search terms are not case sensitive.
- Narrow a Search
-
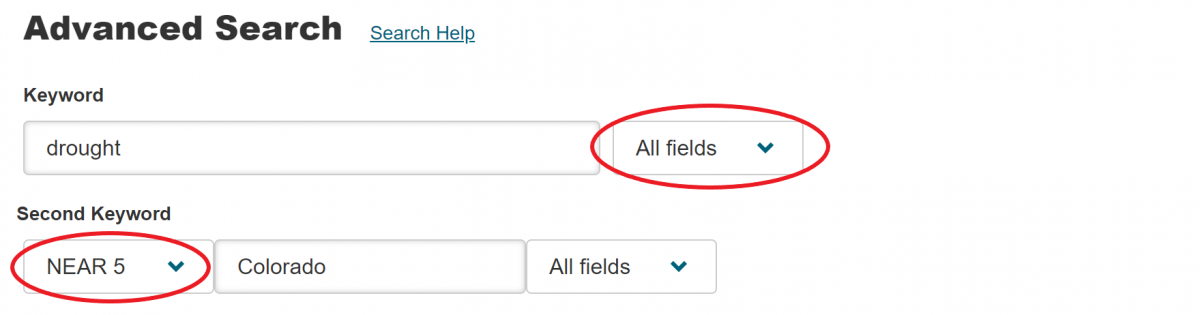
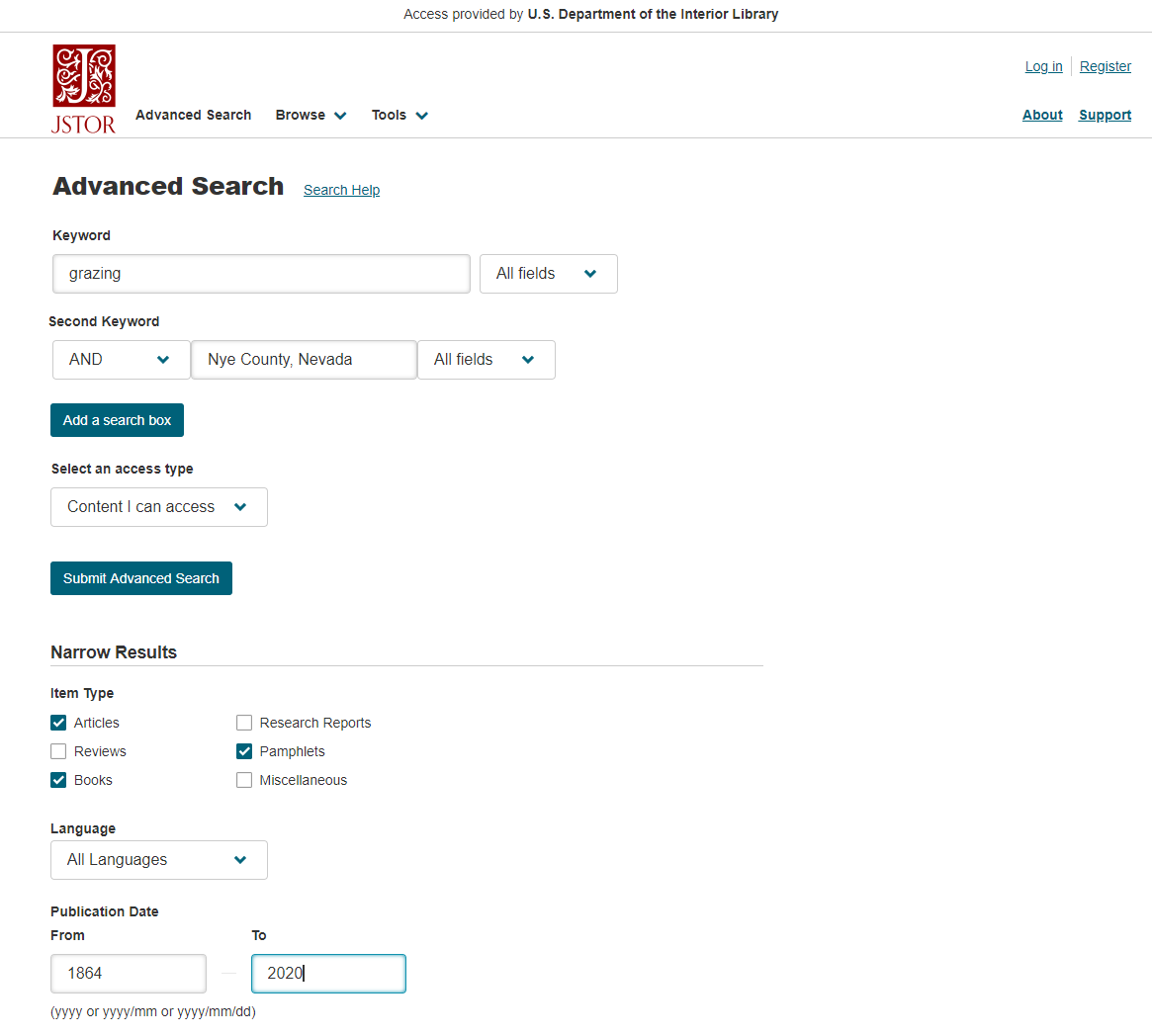
Narrow a search by specifying item types, date range, language, disciplines, and/or publication titles. Click on the plus sign next to a discipline to see a list of associated journal titles, and check the boxes for the journal titles to include in the search.
- Organize Results
-
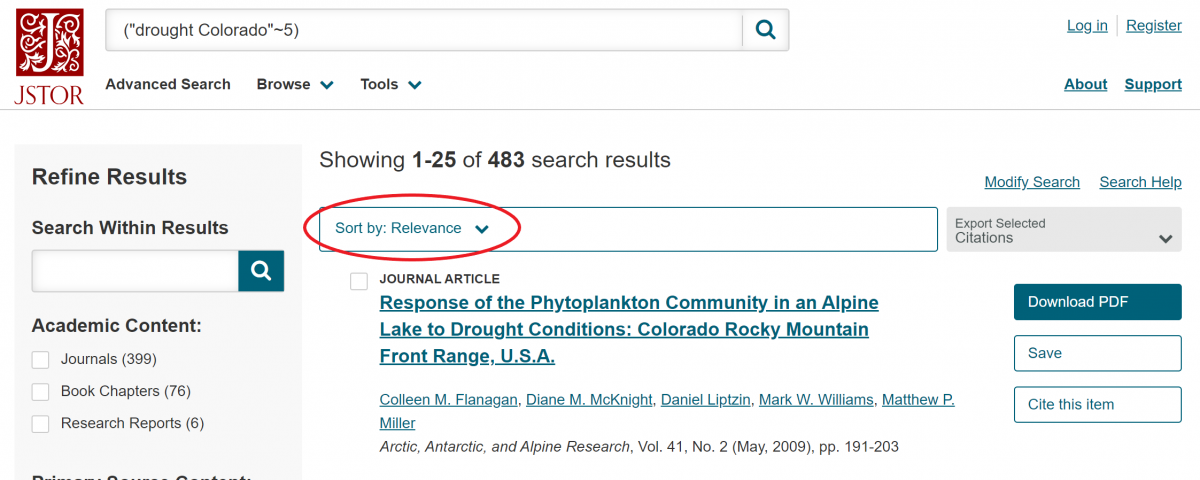
Organize results by sorting by relevance or date and/or changing the number of items shown per page. JSTOR defaults to showing only results to which users have access; to see all results, select All content from the Show drop list. For access to items not available to BLM users through JSTOR, contact the BLM Library at blm_library@blm.gov. To find more of an author's work, click on the author's name in the results list. Results will only include articles in publications held by JSTOR.

- Create Citations
-
Quickly create citations by clicking on the "Cite this item" box to the left of the desired article in the results list. JSTOR provides citations in APA, MLA, and Chicago styles. The citations can then be copy and pasted or exported.
Other tools include viewing the article in PDF format and viewing, exporting, saving, or tracking the citation. To print an article, view or download the PDF first and select the print option from the open PDF. Additional options include references to the selected article and lists of publications by the author in JSTOR and in Google Scholar.

- Analyze Text
-
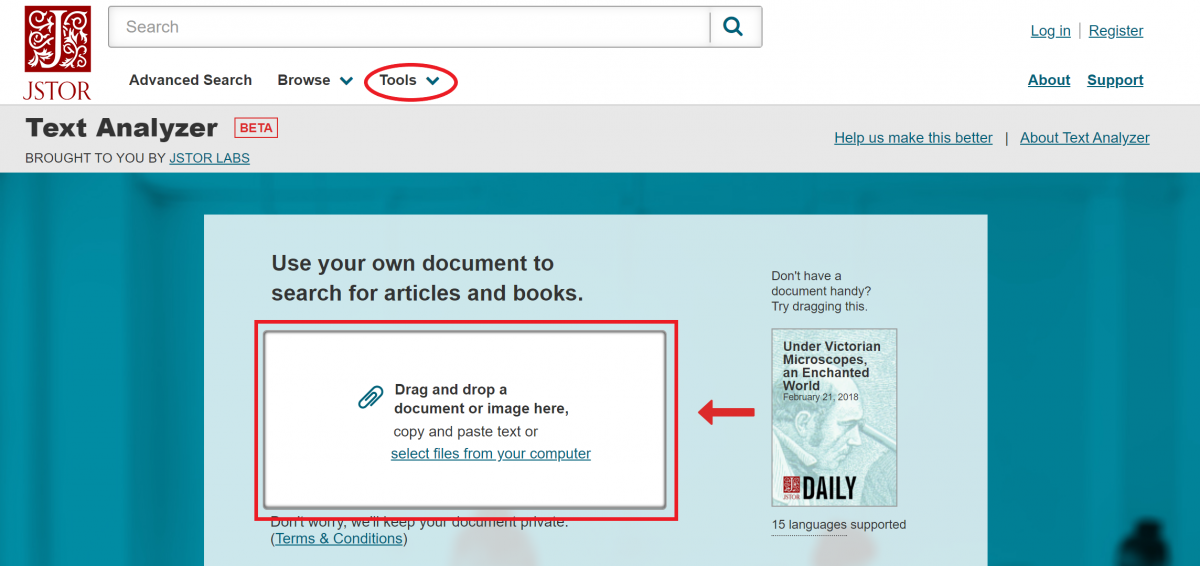
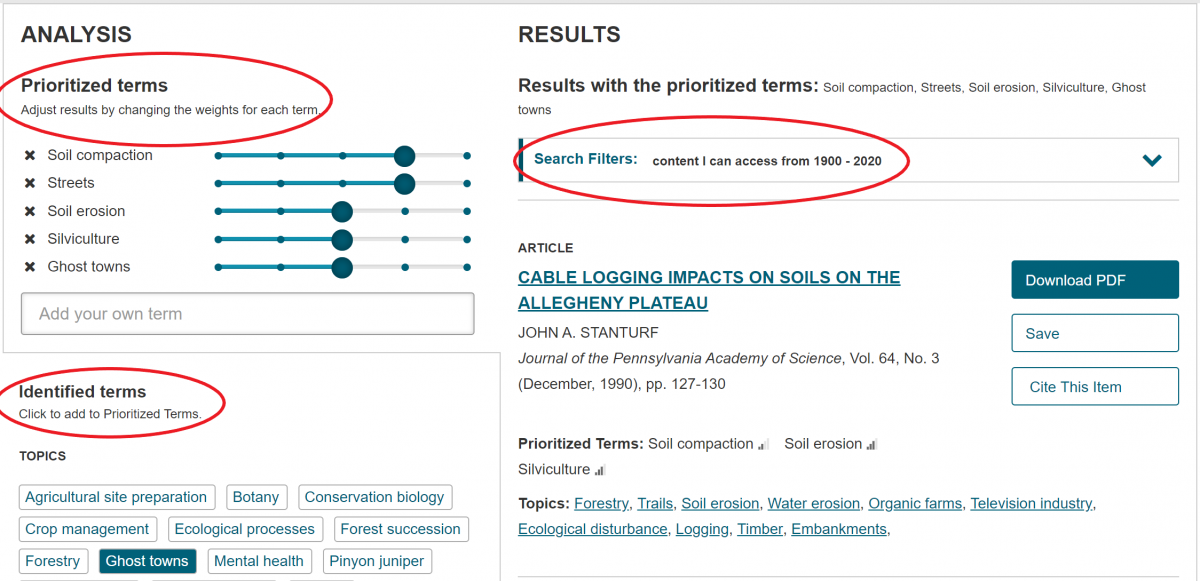
Quickly retrieve an array of relevant articles using JSTOR’s new Text Analyzer tool. Go to Tools --> Text Analyzer to upload any text document (like an article, a white paper that’s still in progress, or a photo of a book page) to find similar content in JSTOR. On the results page, you can reprioritize the identified search terms and add keywords of your own.
This is useful if you’re not having much success using traditional keyword searching or if you want to quickly access articles cited in another document.
Note: Text Analyzer is still in Beta, so it may not always be accurate. Make sure to double check your search results.
- Searching Tips
-
Some final tips for crafting search queries:
Including # (pound sign) or & (ampersand) at the end of a word will search for variations of a word. For example, a search for goose# or goose& will return results that include goose, geese, and gosling. Find words with similar spellings by using ~ (tilde) at the end of a word. For example, a search for Dostoevsky~ will return variant spellings such as Dostoevski, Dostoyevsky, and Dostoyevski. Replace a single letter with ? (question mark) for alternate spellings. For example, a search for globali?ation will return both globalization and globalisation. This is useful for words with different American and British spelling. Use * (asterisk) as a wildcard to replace more than one letter and search for variant endings of a word. For example, bird* will return bird, birds, birding, and other terms starting with "bird." Do not use the wildcard as the first letter or when using quotes around a title or phrase.
Are you ready to test out your new searching skills? Head over to JSTOR to get started.
Although these tips should yield improved results, it's hard to beat a professional librarian for fast and effective searching. For assistance with identifying and accessing publications, contact the BLM librarians at blm_library@blm.gov.