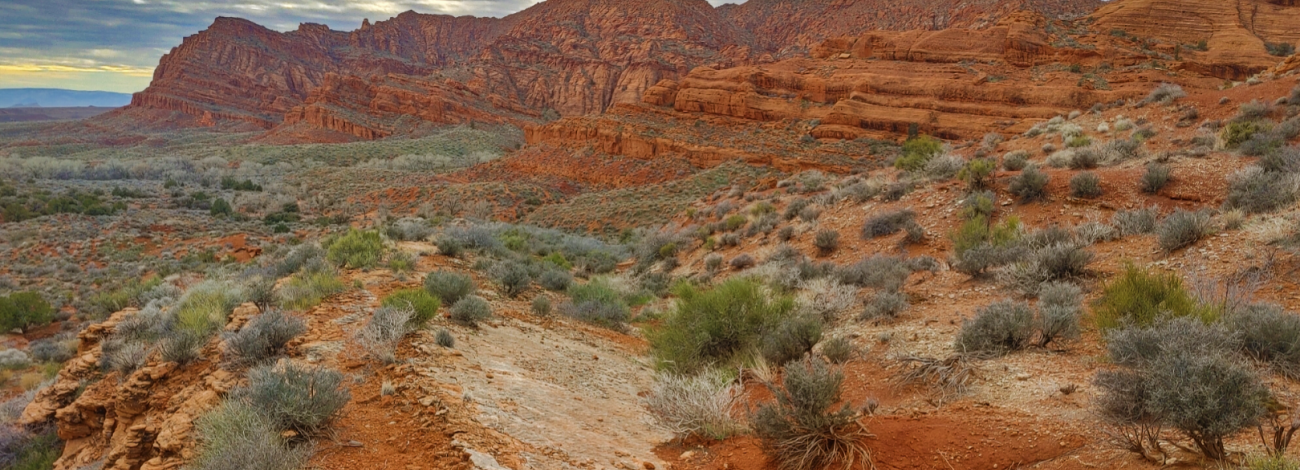
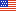
Red Cliffs National Conservation Area
The Red Cliffs National Conservation Area in southwest Utah comprises 45,600 acres of ecological diverse landscapes located at the convergence of the Mojave Desert, Colorado Plateau and Great Basin physiographic regions. The Pine Valley Mountains, part of the Dixie National Forest, lie to the north of the Red Cliffs National Conservation Area, while the communities of Ivins, Santa Clara, St. George, Washington and Leeds surround the southern boundary.
The federally designated Red Mountain Wilderness and Cottonwood Canyon Wilderness areas, within the National Conservation Area, provide outstanding opportunities for solitude, natural quiet, and unconfined recreation.
The Red Cliffs National Conservation Area encompasses critical habitat that sustains high densities of the threatened Mojave Desert tortoise and other Mojave Desert species. The Virgin River, Quail Creek and Leeds Creek provide aquatic habitat for the threatened and endangered native fish of the Virgin River system. Riparian zones along these streams support diverse native species and migratory birds.
Incredible exposures of the Jurassic age Kayenta Formation and Navajo Sandstone are protected within the National Conservation Area and preserve scientifically important dinosaur tracks and trackways, bone beds, plant fossils and petrified wood.
The Red Cliffs National Conservation Area conserves and protects these incredible resources for the benefit and enjoyment of present and future generations. More than 130 miles of designated hiking, mountain biking and equestrian trails are available for public use within the Red Cliffs National Conservation Area and Red Cliff Recreation Area.